1. Policy for organizing the curriculum
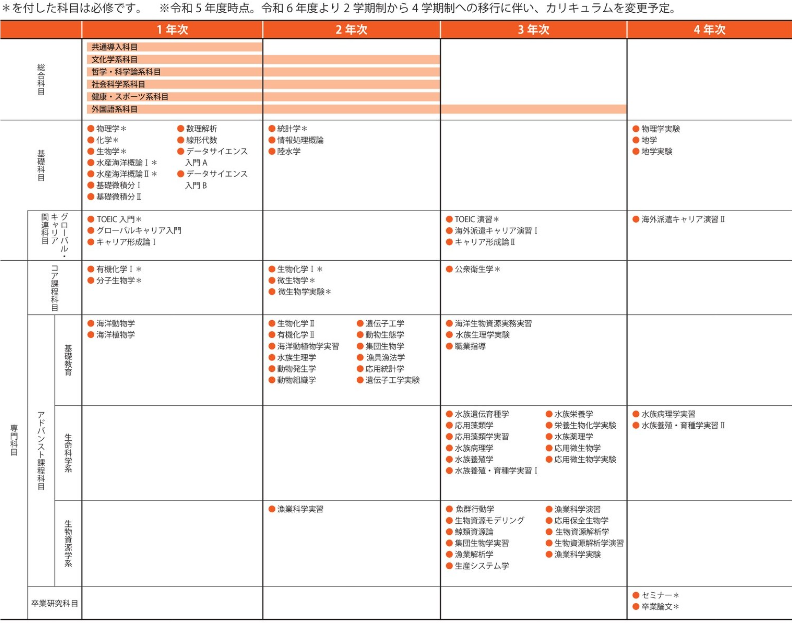
In the Department of Marine and Biological Resources, we offer ``general subjects'', ``specialist entrance subjects'', and ``specialized subjects (core courses)'' in order to help students acquire the four basic skills and abilities listed in ``2'' below. ” and “Specialized subjects (advanced course subjects)” are organized systematically. We have established ``General Subjects'' to acquire a wide range of knowledge and language skills, ``Specialization Introductory Subjects'' to learn a wide range of basic sciences, and ``Specialized Subjects (Core Curriculum Subjects)''. As technology becomes more diverse and sophisticated, we will enrich the basic skills necessary to understand it. On top of that, we have students learn specialized knowledge in ``specialized subjects (advanced course subjects).'' ``Advanced Course Subjects'' are the basics of all fields in this department, which are studied in the lower grades, and then cultivate deeper knowledge and become specialized. Students will systematically learn through "Advanced Course Subjects (Life Science)" and "Advanced Course Subjects (Biological Resources Science)" to develop their abilities, and will connect with graduate school education. . Furthermore, ``Global Career Related Subjects'' will help students connect smoothly to the international community, industry, and other societies.
2. Policies regarding educational content and educational implementation methods
The class subject categories are "general subjects," "specialized introductory subjects," "specialized subjects (core curriculum subjects)," and "specialized subjects (advanced course subjects (basic education))." , ``Advanced Course Subjects for Specialized Subjects (Life Science),'' ``Advanced Course Subjects for Specialized Subjects (Biological Resources Science),'' and ``Global Career Related Subjects,'' with lectures and exercises. , conduct experiments and practical training.
(1)Specialized knowledge
In order for all students in the department to acquire specialized knowledge that is the basis for all fields of the department, we offer "Specialized Subjects (Advanced Courses (Basic Subjects)") from the first to third years. will be carried out. Furthermore, we use laboratory scientific methods to understand life phenomena at the genome, cell, and individual organism levels, and field scientific methods to understand the relationship between the environment and living things and ecosystems, and apply applied scientific knowledge. A curriculum that systematizes the methods will be offered mainly in the third year as specialized subjects (Advanced Course Subjects (Life Science)) and Advanced Course Subjects (Biological Resources Science). Through experiments, practical training, and exercises, students actually experience the series of processes of understanding problems, observing target organisms, analyzing them, and logically considering them, as well as learning how to collaborate with others and lead. .
(2) Rich internationality and wide-ranging education
With the aim of cultivating a wide range of knowledge, logical thinking ability, cultural background, international perspective, communication skills, and presentation skills, we carry out ``general subjects,'' and also prepare students for English qualification exams, study abroad, and We will conduct "Global Career Related Subjects" related to each career development. In the first and second years, students are taught systematic basic knowledge of natural science, mathematical science, humanities and social science, and basic information technology, which are the foundation for learning specialized subjects. ``Specialization Entrance Subjects'' and ``Specialization Subjects (Core Curriculum Subjects)'' will be held.
(3) Ability to think and make decisions independently
In order to acquire the foundation and ability to think logically and make accurate judgments based on a variety of information, we provide exercises, experiments, practical training, and A 4th year seminar and graduation thesis will be held. Furthermore, in order to help students acquire the ability to make ethical decisions, we provide education related to researcher ethics as part of the fourth-year seminar.
(4) Practical skills that can be used in the field
In order to enable students to effectively utilize knowledge, data, and information technology in various situations, and to acquire the applied and practical skills to integrate them and make use of them in the marine field, we offer a seminar and a graduation thesis in the fourth year. We aim to develop the ability to identify issues that need to be solved, plan a path to a solution, and carry out and verify plans based on the plan. In addition, we offer ``Global Career-related Subjects'' to help students connect smoothly with the international community, industry, and other societies.
3. Policy regarding evaluation method of learning outcomes
In all subjects, learning outcomes and achievement of goals will be rigorously evaluated through exams, reports, presentations, etc.