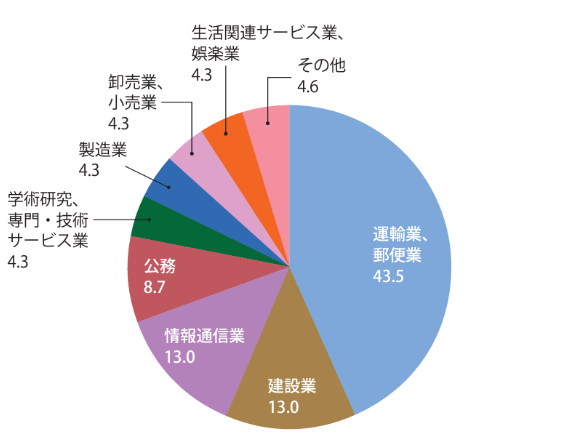
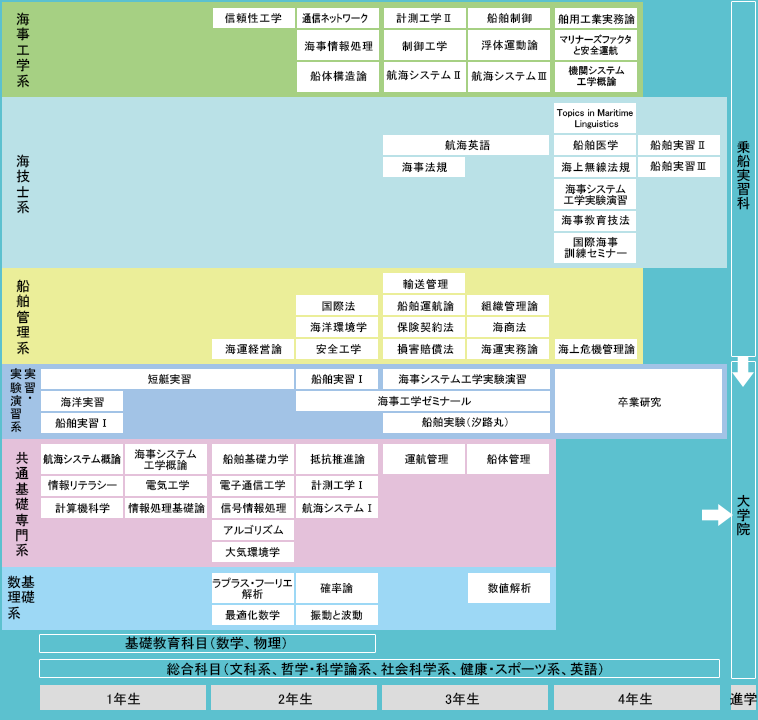
1. Policies for organizing and implementing the curriculum
In the Department of Maritime Systems Engineering, in order to learn the five abilities listed in the graduation certificate and degree award policy (diploma policy), we have three skills: culture, philosophy and science, social science, foreign language, and health and sports. We will systematically organize the study of general subjects consisting of mathematics, physics, chemistry, information, and various foreign languages, and specialized subjects. A curriculum will also be created to enable the acquisition of the third-class marine engineer (navigation) qualification.
?Throughout the school year, we will conduct learning to acquire a wide range of knowledge, rich humanity, advanced technology, and the ability to be active internationally.
-Especially in the first year, learning will be based on general subjects and specialized introductory subjects. In addition, to ensure a smooth transition into university education, we will also provide introductory subjects in the first year.
?Especially in the second and third years, students will gradually transition from studying mainly introductory subjects to studying mainly advanced specialized subjects.
?Especially in the 4th year, based on the basic skills acquired from the 1st to 3rd year, students acquire independence, creativity, and presentation skills, and acquire a wide range of knowledge and deep specialized knowledge. Provide guidance on graduation research so that students can apply it to various tasks.
- At the same time, study will be carried out to enable the acquisition of the qualification of third-class marine engineer (navigation).
2. Policies regarding educational content, educational implementation methods, and evaluation methods
(1) Broad perspective and cultural background
(Learning content) To equip students with a wide range of perspectives, abilities, and cultural background that form the basis of international exchange.
(Study method) Students will study a wide range of general subjects and specialized introductory subjects, mainly in their first and second years. In addition, in order to smoothly enter university education, students will be required to study introductory subjects in their first year.
(Method of evaluating learning outcomes) Objectively evaluate the degree of acquisition of a wide range of knowledge and cultural background through examinations, reports, deliverables, etc. according to the characteristics of the subject.
(2)Communication skills
(Learning content) To help students acquire communication skills backed by a wide range of knowledge and an international perspective, which are necessary for engineers.
(Learning method) Through a variety of foreign language subjects, experiments, practical training, and seminar report writing, graduation thesis writing, and graduation thesis presentation, students will acquire diverse communication skills that will enable them to collect and disseminate necessary information. Let them study.
(Method of evaluating learning outcomes) The level of communication skill acquisition will be objectively evaluated through reports, graduation thesis presentations, etc., depending on the characteristics of the subject.
(3)Specialized knowledge/problem-solving ability
(Learning content) Possess and utilize specialized knowledge of maritime technology, including ship operation and maintenance management, design and development of maritime-related equipment, equipment, and systems, and design and management of ports and routes. and develop the ability to solve problems.
(Study method) Students will systematically study introductory and specialized subjects, from basics to applied subjects, to fully acquire a wide range of specialized knowledge. We will have students study subjects such as experiments, practical training, seminars, and graduation research that will help them develop problem-finding, problem-solving, and creativity skills.
(Method of evaluating learning outcomes) Objectively evaluate the degree of acquisition of specialized knowledge and problem-solving ability using tests, reports, deliverables, etc., depending on the characteristics of the subject.
(4)Practical instruction/leadership
(Learning content) To help students acquire the practical leadership skills and leadership required as leaders in society.
(Learning method) Have students study subjects such as experiments, practical training, seminars, and graduation research that can foster leadership and the ability to exercise leadership and leadership in a group.
(Method of evaluating learning outcomes) Depending on the characteristics of the subject, the level of practical instruction and leadership skills will be objectively evaluated through reports, graduation thesis presentations, graduation thesis, etc.
(5) Ability to make decisions and act on one's own
(Learning content) To acquire the ability to proactively tackle challenges, think logically, and make accurate judgments and actions.
(Learning method) Have students study subjects such as experiments, practical training, seminars, and graduation research that will help them develop the ability to make decisions and take action on their own.
(Method of evaluating learning outcomes) Depending on the characteristics of the subject, the degree to which students have acquired the ability to make decisions and act on their own will be objectively evaluated using reports, graduation theses, etc.